مقالات IranBIM, مقالات خارجی
BIM چیست؟ فواید بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز چگونه است ؟
فواید بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز چیست ؟
BIM بازیکن ستاره فعلی در صنعت ساخت و ساز است. (بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز) اگرچه این تکنولوژی حدود یک دهه است که وجود دارد، اما بسیاری از شایعات در مورد BIM در این زمینه برای دو سال گذشته ایجاد شدهاست. همه ما میدانیم که آن برای مدلسازی اطلاعات است ، اما BIM واقعا چیست ؟
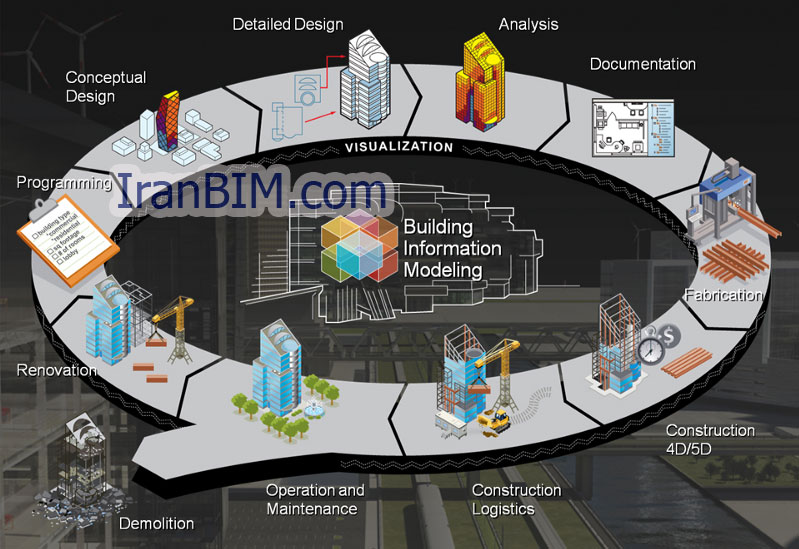
BIM فرآیندی است که در طول تولید و مدیریت اطلاعات فیزیکی و عملکردی یک پروژه انجام میشود. خروجی این فرآیند چیزی است که ما به آن به عنوان مدلهای اطلاعات ساختمان یا ساختمان اشاره میکنیم که در نهایت فایلهای دیجیتال هستند که هر جنبه از پروژه را توصیف میکنند و تصمیمگیری را در طول یک چرخه پروژه پشتیبانی میکنند. این تصور وجود دارد که BIM چیزی بیش از مدل سازی سه بعدی نیست اما در واقع شامل بیش از این است .
BIM و زیرمجموعههای سیستمهای BIM و ویژگیهای مشابه بیشتر از تنها D3 (عرض، ارتفاع و عمق) اما ممکن است شامل ابعاد بیشتر مانند D4) زمان (، D5(هزینه) ، وحتی D (6مانند عملیات ساخت) باشد. ( Smith 2014)
BIM چیست ؟
بنابراین، از لحاظ فنی، مدلسازی اطلاعات چیست؟ این تعریف کمیته استاندارد اطلاعات ساختمان ایالاتمتحده آمریکا است:
مدل سازی اطلاعات ساختمان ( BIM ) نمایش دیجیتالی ویژگیهای فیزیکی و عملکردی یک ساختمان است.
BIMیک منبع دانش مشترک برای اطلاعات در مورد یک ساختمان است که یک پایه قابلاعتماد برای تصمیمگیری در طول چرخه عمر آن را تشکیل میدهد ؛ و همانطور که از اولین مفهوم برای تخریب تعریف شدهاست – NBIMS) .ایالاتمتحده، ۲۰۱۶ )
به نظر میرسد که این تعریف همان چیزی باشد که بقیه صنعت ساختوساز در سرتاسر جهان به رسمیت میشناسد( Smith، ۲۰۱۴)
همان طور که قبلا گفته شد ، BIM بیش از یک هندسه را پوشش میدهد- آن ” روابط فضایی،تحلیل نور، اطلاعات جغرافیایی، و کمیت و ویژگیهای اجزای ساختمان را پوشش میدهد “( ایستمن، ۲۰۰۹ (.
اشیا و ابزارهای BIM
آنچه BIM است، نمایش یک طراحی به عنوان ترکیبی از ” اشیا ” – مبهم و تعریفنشده، اشکال جامد یا محصول -فضای محور ( مانند شکل یک اتاق) ، که هندسه، روابط و ویژگیهای آنها را حمل میکند ). ایستمن، ۲۰۰۹ )
ابزارهای طراحی BIM اجازه استخراج دیدگاههای مختلف از یک مدل برای تولید در بین چیزهای دیگر را میدهد. این دیدگاههای مختلف به طور خودکار سازگار هستند، چرا که آنها از یک تعریف واحد از هر ” نمونه هدف ” میآیند) . ایستمن، ۲۰۰۹ )
اشیا همچنین به صورت پارامترها و روابط با اشیا دیگر تعریف میشوند، به طوری که اگر تغییراتی در یک شی مرتبط وجود داشته باشد ، به صورت خودکار یا مجاور خود را تغییر داده یا تنظیم میکند. (ایستمن، ۲۰۰۹)
هر عنصر یک مدل ساختمان میتواند ویژگیهایی را به طور خودکار انتخاب کرده و به آنها سفارش دهد که در آن برآوردهای هزینه و پیگیری مواد و سفارش را می توان ارایه کرد .( ایستمن، ۲۰۰۹ )

(عکس شماره ۳)
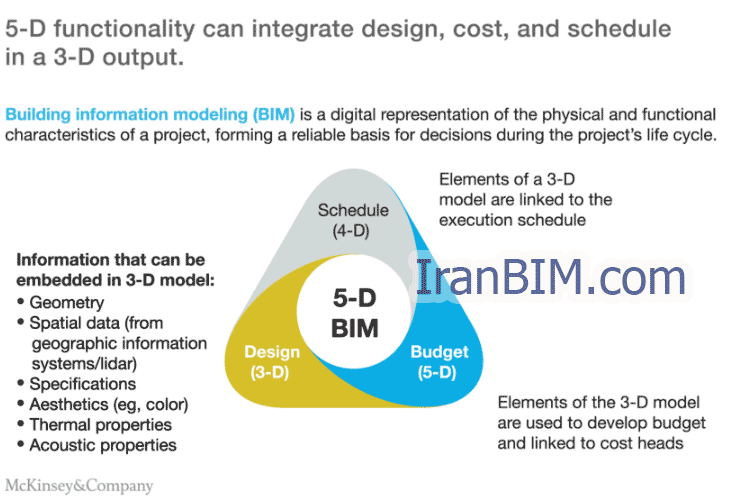
مدل ۵ بعدی و ابعاد مختلف
زیرمجموعههای مختلف BIM به لحاظ ابعاد ۳D (مدل جسم(، ۴D (هزینه)، ۶D (عملیات) ، ) ۷D پایداری) ، و حتی ) ۸D ایمنی ( توصیف میشوند. ( Smith۲۰۱۴ )
این ظرفیت چند بعدی BIM به عنوان ” nD ” تعریف شدهاست به عنوان یک تعداد نامحدود از ابعاد را می توان به مدل ساختمان اضافه کرد (Smith – ۲۰۱۴ )
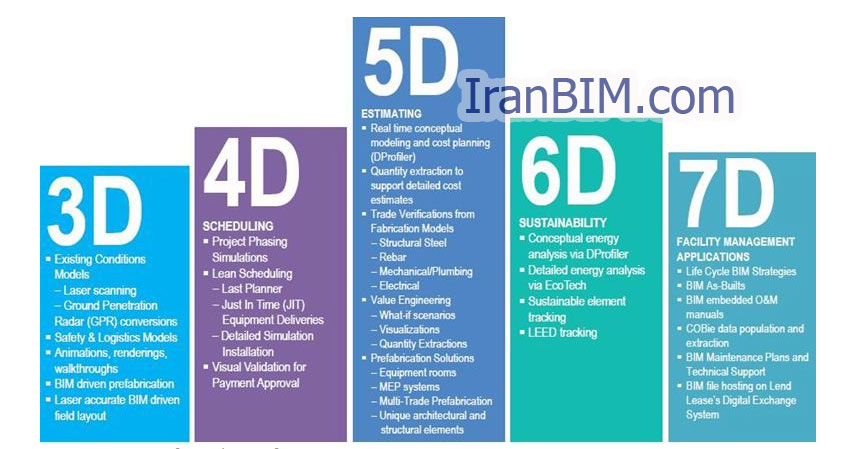
مدل ۴ بعدی فعالیتهای ساخت وساز را به برنامههای زمانی و تصاویر سهبعدی پیوند میدهد که منجر به شبیه سازی گرافیکی زمان واقعی پیشرفت ساخت وساز میشود.
بعد ” زمان ” ارزیابی برنامه ریزی گردش کار و گردش کار یک پروژه را ممکن میسازد. هر کسی که در این پروژه مشارکت داشته باشد میتواند به سادگی و به طور موثر تصویرسازی،تحلیل و ارتباط را در ابعاد زمانی، فضایی و زمانی پیشرفت ساختوساز ترسیم کند. این منجر به برنامههای بهتر، چیدمان سایت و طرحهای منطقی ای میشود که بهبود بهرهوری را تولید میکنند . مدل ۵ بعدی، بعد از ” هزینه ” را به مدل BIM اضافه میکند و تولید فوری بودجههای هزینه و نمایش مالی این مدل در برابر زمان را میدهد.
این امرصحت برآوردهای مورد نظر را بهبود میبخشد ، حوادث اختلاف را به حداقل میرساند، و اجازه میدهد مشاوران هزینه زمان بیشتری را صرف بهبود ارزش کنند.
بعد ششم ۶D
مدل ۶D به مدیریت امکانات اجازه اضافه کردن به BIM را میدهد. اضافه کردن توصیف غنی عناصر ساختمان و خدمات مهندسی با توصیفا ت دقیق به هندسه، روابط، و قابلیتهای دارایی BIM را یک پایگاه داده مدیریت امکانات کامل میسازد. مدل ۷ بعدی مولفههای پایداری را در BIM گنجانیده است – این مدل به افراد / طراحان اجازه میدهد تا اهداف کربن را برای یک عنصر خاص از یک پروژه ملاقات کرده و تصمیمات را ارزیابی کرده و گزینهها را مقایسه کنند . شکل ۸D جنبههای ایمنی را هم در طراحی و هم فرآیند ساخت به همراه دارد.
BIM و فنآوریهای متعدد با هم فرصتهایی برای پروژه فراهم میکنند اما برای مدیر پروژه نیز چالشهایی وجود دارد. از آنجا که اتوماسیون به طور فزاینده ای در تعین درصنعت ساخت وساز مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد، مدلهای BIM نیاز به سازگاری با اجزای مدیریتی پیچیده تر دارد که مدل سازی هزینه ۴ بعدی و مدلسازی هزینه ۵ بعدی را در بر میگیرد و این اطلاعات را با تیم پروژه در یک رویکرد تحویل پروژه یکپارچه به اشتراک میگذارد.
با این حال، BIM در مورد نرمافزار و فنآوری جدید نیست. این روش به یک روش جایگزین برای تفکر و یک رویکرد متفاوت برای تهیه و تحویل پروژه نیاز دارد. انتقال از رویکرد سنتی مشارکت پروژه با استخرهای اطلاعاتی جداگانه و تکنولوژیهای نرمافزاری ناسازگار به یک پلت فرم مشترک که شرکت کنندگان میتوانند در آن به اشتراک گذاشته و بر روی همان اطلاعات کار کنند، ضروری است. BIM ابزار نهایی برای این است.( Smith، ۲۰۱۴ )
تاریخچه مختصر BIM
ایده BIM در دهه ۷۰ تصور شد و ابتدا سیستم توصیف ساختمان ( واحد خنثیسازی بمب ) نامیده شد. ( ایستمن و همکاران، ۱۹۷۴ )
اصطلاح ” مدل ساختمان ” اولین بار در سال۱۹۸۵ در یک مقاله طراحی معماری روی طراحی با کمک کامپیوتر و طراحی به کمک کامپیوتر استفاده شد ( ruffle، ۱۹۸۵ )
و در سال ۱۹۹۲، اصطلاح ” مدل اطلاعات ساختمان ” اولین بار در یک مقاله در مورد اتوماسیون در ساخت وساز مورد استفاده قرار گرفت ( وان Nederveen et al .،۱۹۹۲)
با این حال ، تا ۱۰ سال بعد، زمانی که عبارت مدلسازی اطلاعات و مدل اطلاعات ساختمان (از جمله استفاده از (BIM به طور عمومی استفاده شد. در سال ۲۰۰۲ زمانی کهAutodesk مقالهای با عنوان ” مدلسازی اطلاعات ساختمان ” منتشر کرد و توسعه دهندگان نرمافزار و فروشندگان مختلف در این حوزه درگیر شدند و این اصطلاح به عنوان نامی مشترک برای نمایش دیجیتالی فرآیند ساخت استاندارد شد ( Laiserin، ۲۰۰۸)
اصطلاحات دیگری ازفرمت مشابه توسط سازندگان مختلف استفاده شدهاست – آنها ” ساختمان مجازی ” باGraphisoft و ” مدلهای پروژه یکپارچه ” توسط سیستمهای Bentley ” بودند. بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز

(عکس شماره ۶)
Graphisoft راهحل سیستم اولیه را طولانیتر از رقبا در بازار ایجاد کرده و مسئول ArchiCAD،که در آن زمان ” یکی از کاملترین راهحلهای BIM در بازار بود ” بود Laiserin، ۲۰۰۳ )
این اولین اجرای BIM در سال ۱۹۸۷ است و اولین محصول با کمک کامپیوتر ( CAD ) در یک کامپیوتر شخصی است که میتواند ۲D و ۳ بعدی را ایجاد کند ، و اولین محصول BIM تجاری برای کامپیوترهای شخصی ” ( فوربس etal، ۲۰۱۰)
تاثیر BIM بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز
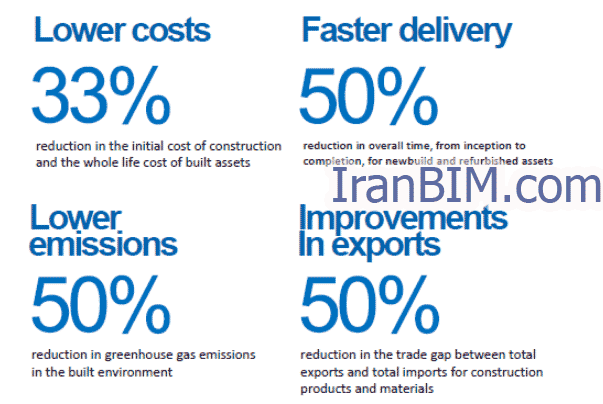
در گزارش مکنزی، یک مطالعه نشان داد که ۷۵ ٪ شرکتهایی که BIM را اتخاذ کردهاند بازدههای مثبتی را در سرمایهگذاری خود با چرخههای عمر پروژه کوتاه تر و صرفهجویی در کاغذ و هزینههای مادی گزارش کردهاند. به دلیل این مزایا، دولتهای مختلف مانند بریتانیا ، فنلاند و سنگاپور استفاده از BIM برای پروژههای زیرساخت عمومی را اجباری میکنند . (Agarwal etal)، سال ۲۰۱۶ )
در مطالعات تخصصی کوچک، BIM به نظر میرسد بهره وری را در کار افزایش میدهد. در یک مطالعه شامل یک شرکت قرارداد کوچک ، تاثیر BIM بر بهره وری نیروی کار تعیین شد و یافتههای نشان داد که ۷۵ ٪ تا ۲۴۰ ٪ افزایش در بهره وری نیروی کار برای مدل سازی شده و پیشساخته ( Poirier، ۲۰۱۵ ) نشان دادهاند.
بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز!
(برای حرفه ایها ) معماران، surveyors، مهندسی ( درگیر در یک پروژه زیر ساخت ، BIM اجازه میدهد تا یک مدل اطلاعات مجازی از تیم طراحی به پیمان کار اصلی و پیمانکاران فرعی وسپس به مالک / اپراتور با هر متخصص خاص متخصص در یک مدل به اشتراک گذاشته شود. کل سیستم برای کاهش تلفات اطلاعات طراحی شده است که به طور سنتی روی میدهد به خصوص زمانی که یک تیم جدید یک پروژه را بر عهده میگیرد.
همچنین اطلاعات گستردهای از ساختارهای پیچیده فراهم میکند . ( ایستمن ، ۲۰۰۹ )
(عکس شماره ۸)
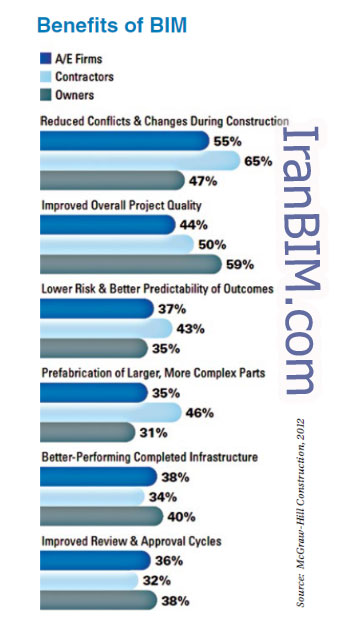
استفاده از راهکارهای مدلسازی اطلاعات ساختمان در بخش ساخت وساز منجر به کار با کیفیت بالاتر، سرعت و بهره وری بیشتر، و هزینههای کم تر برای افراد حرفه ای از نظر طراحی ، ساخت وساز، و بهره برداری از ساختمانها شد . Laiserin )، ۲۰۰۲ )
کیفیت عالی
BIM به انعطاف پذیری در اکتشاف و تغییرات در فرآیند طراحی یا سندسازی پروژه در هر زمانی بدون دردسر برای تیم طراحی اجازه میدهد. این منجر به حداقل سازی زمان هماهنگی و کنترل دستی میشود که تیم طراحی را قادر میسازد تا زمان بیشتری برای حل مشکلات معماری واقعی داشته باشد. ابزارهای مدلسازی مشترک کنترل نزدیکی بر تصمیمات فنی و مفصل در رابطه با اجرای طراحی دارند.
رکورد دیجیتال نوسازی ساختمان برنامهریزی ومدیریت را بهبود میبخشد.
سرعت بیشتر!
BIM این امکان را فراهم میکند که طراحی و سندسازی به صورت همزمان به جای سریالی انجام شود . برنامه، نمودارها، طراحی ، برآورد ، مهندسی ارزش، برنامهریزی و دیگراشکال ارتباطات کاری به طور پویا ایجاد میشوند در حالی که کار در حال پیشرفت است.
BIMاجازه سازگاری مدل اصلی به تغییرات مانند شرایط سایت و غیره را میدهد.
هزینه پایینتر!
استفاده از BIM اجازه کار بیشتر توسط یک تیم کوچکتر را میدهد. این به معنای هزینههای پایین تر و miscommunications کمتر است. زمان و پول کمتری در فرآیند ومدیریت به دلیل کیفیت اسناد بالاتر و برنامه ریزی ساختوساز بهتر خرج میشوند.
پتانسیل آینده بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز
BIM یک تکنولوژی نسبتا جدید به خصوص در بخش ساختوساز است، یک صنعت به طور متوسط برای سازگاری با تغییر کند است . حامیان BIM ادعا میکنند که در آینده نزدیک، مقدار زیادی از این مقدار را ارائه میکند. (رحمانی Asl et al ۲۰۱۳ )
- تجسم کردن تجسم.
- بهبود بهرهوری از طریق بازیابی آسان اطلاعات.
- افزایش هماهنگی اسناد ساختوساز.
- ارتباط دادن اطلاعات حیاتی مانند فروشندگان مواد خاص، محل جزئیات و مقادیر مورد نیازبرای مناقصات
- افزایش سرعت تحویل.
- کاهش هزینههای کلی.
مدلسازی اطلاعات ساختمان و فنآوریهای quantities خودکار میتواند این صنعت را بافرصتهای مهم برای بالا بردن کیفیت صنعت به سطح بالاتر و پیچیدهتر فراهم کند. با داشتن توانایی شبیهسازی دامنه گزینههای داده با مشاوره هزینه زمان واقعی و ادامه در تمام مراحل طراحی، ساختوساز، و مراحل عملیاتی، BIM قطعا اقدامات ساخت وساز را با ارزش بالاتر انجام خواهد داد.
بیم در صنعت ساخت و ساز
این مقاله اولین مقاله در مجموعهای از مدلسازی اطلاعات ساختمان ( BIM ) است. مکمل این مطالعه با مقالاتی در مورد تاریخچه BIM، نقشها در یک چرخه پروژه BIM، چالشها وپتانسیلهای این فنآوری ساختوساز نوظهور، مفاهیم آتی آن و کاربرد مشترک آن.
Category: Quality management plan constructionBy Thomas Goubau
What is BIM?
BIM is the current star player in the construction industry. Although the technology has been around for about a decade, a lot of buzz has been created about BIM in the field for the past two years. We all know that it stands for building information modelling but what is BIM really? BIM is the process spanning the generation and management of the physical and functional information of a project.
What are its Benefits to the Construction Industry?
The output of the process are what we refer to as BIMs or building information models which are ultimately digital files that describe every aspect of the project and support decision-making throughout a project cycle. It has been thought that BIM is nothing more than 3D modelling but it actually involves more than that. BIM and the subsets of BIM systems and similar technologies feature more than just 3D (width, height, and depth) but may include further dimensions such as 4D (time), 5D (cost), and even 6D (as-built operation) (Smith, 2014).
Image courtesy of Autodesk
What is BIM?
So, technically, what is building information modelling? This is the US National Building Information Model Standard Project Committee’s definition:
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. A BIM is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life-cycle; defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition (NBIMS-US, 2016).
This definition seems to be what the rest of the construction industry recognize across the globe (Smith, 2014). As mentioned earlier, BIM covers more than just geometry — it covers “spatial relationships, light analysis, geographic information, and quantities and properties of building components” (Eastman, 2009).
BIM Objects and Tools
What BIM is, is representing a design as combinations of “objects” — vague and undefined, generic or product-specific, solid shapes or void-space oriented (like the shape of a room), that carry their geometry, relations and attributes (Eastman, 2009). BIM design tools allow the extraction of different views from a model for production of drawing among other things. These different views are automatically consistent, as they come from a single definition of each “object instance” (Eastman, 2009).
Objects are also defined as parameters and relations to other objects, so that if there are changes in a related object, dependent or adjacent ones will automatically change or adjust (Eastman, 2009). Each element of a building model can carry attributes to automatically select and order them where cost estimates and material tracking and ordering can be provided (Eastman, 2009).
Image courtesy of Warren and Mahoney
The 5D Model and Various Dimensions
The various subsets of BIM are described in terms of dimensions — ۳D (object model), 4D (time), 5D (cost), 6D (operation), 7D (sustainability), and even 8D (safety) (Smith, 2014). This multidimensional capacity of BIM has been defined as “nD” modeling as an almost infinite number of dimensions can be added to the building model (Smith, 2014).
Time schedules
The 4D model links construction activities to time schedules and 3D images that result to a real-time graphical simulation of the construction progress. The “time” dimension enables the evaluation of the buildability and workflow planning of a project. Everyone involved in the project can easily and effectively visualize, analyze, and communicate problems in the sequential, spatial, and temporal aspects of the construction progress.
۴D
This results to better schedules, site layout and logistic plans that generate improvement in productivity. The 5D model adds the dimension of “Cost” to the BIM model and allows instant generation of cost budgets and financial representations of the model against time. This improves the accuracy of estimates, minimizes dispute incidents that CAD data usually cause, and allows cost consultants to spend more time on improving value.
The 6D Model
The 6D model enables facilities management to be added to the BIM. Adding rich description of building elements and engineering services with elaborate descriptions to the geometry, relationships, and property capabilities makes the BIM a perfect facilities management database. The 7D model incorporated sustainability components to the BIM — it allows for professionals/designers to meet carbon targets for a specific element of a project and validate decisions or test and compare options. The 8D incorporates safety aspects in both the design and the construction process.
BIM Technology
BIM and allied quantities technologies provide opportunities for the project but also challenges for the project manager. As automation is increasingly used in quantification in the construction industry, BIM models will need to adapt accordingly to allow for more sophisticated management components that incorporate 4D time and 5D cost modelling and sharing these information with the project team in an integrated project delivery approach.
BIM is just not about new software
However, BIM is just not about new software and technology. It requires an alternative way of thinking and a different approach to project procurement and delivery. It is an imperative to move from the traditional approach of project participation with separate information pools and incompatible software technologies to one that is totally integrated with a common platform where participants can share and work on the same information. The BIM is the ultimate tool for this (Smith, 2014).
A Brief BIM History
The idea of BIM was conceptualized in the 70s and was initially called the Building Description System (BDS) (Eastman et al., 1974). The term “building model” was first used in 1985 in an architectural design paper on computer-aided drawing and computer-aided design (Ruffle, 1985). And in 1992, the term “building information model” was first used in a paper discussing automation in construction (van Nederveen et. al, 1992). It wasn’t until 10 years later, though, when the terms building information modeling and building information model (including the acronym BIM) became popularly used.
BIM summery
It was in 2002 when Autodesk published a paper entitled “Building Information Modelling” and various software developers and vendors got involved in the field and the term was standardized to mean as the common name for digital representation of the building process (Laiserin, 2008). Other terminologies of similar format have been used by different makers — they were “Virtual Building” by Graphisoft and “Integrated Project Models” by Bentley Systems.
Building Information Modeling
Graphisoft developed early system solutions longer than the competitors in the market and was responsible for ArchiCAD, which was then “one of the most mature BIM solutions in the market” (Laiserin, 2003). It was regarded as the first BIM implementation in 1987 and was the “first computer-aided design (CAD) product on a personal computer able to create 2D and 3D geometry, and the first commercial BIM product for personal computers” (Forbes et.al, 2010).
BIM Impact in the Industry
In a McKinsey report, one study found that 75% of companies that have adopted BIM reported positive returns on their investment with shorter project life cycles and savings on paperwork and material costs. Because of these benefits, various governments like Britain, Finland, and Singapore, mandate the use of BIM for public infrastructure projects (Agarwal et.al, 2016).
In small specialty studies, BIM appears to be increasing productivity in labor. In a study involving a small contracting enterprise, the impact of BIM on labor productivity was quantified and findings demonstrated a 75% to 240% increase in labor productivity for modeled and prefabricated areas (Poirier, 2015).
BIM for professionals
For the professionals (architects, surveyors, engineers) involved in an infrastructure project, BIM allows for a virtual information model to be communicated from the design team to the main contractor and subcontractors and then to the owner/operator with each specific professional adding specific data to the single-shared model. The whole system is designed to reduce information losses that traditionally occur especially when a new team takes over a project. It also provides extensive information of complex structures (Eastman, 2009).
-
Higher Quality
- BIM allows for flexibility in the exploration and changes to the project design or documentation process at any time without any hassle to the design team. This results to minimized coordination time and manual checking that enables the design team to have more time solving real architectural problems. Common modelling tools provide close control over technical and detailed decisions regarding design execution. The digital record of building renovations improves planning and management.
-
Greater Speed
- . BIM enables for design and documentation to be done concurrently instead of serially. Schedules, diagrams, drawings, estimating, value engineering, planning, and other forms of work communication are created dynamically while work is progressing. BIM allows for adaptation of the original model to changes like site conditions, etc.
-
Lower Cost
- Using BIM allows for more work to be done by a smaller team. This means lower costs and lesser miscommunications. Less time and money are spent in process and administration because of higher document quality and better construction planning.
-
Future Potential
BIM is a relatively new technology especially in the construction sector, an industry typically slow to adapt to change. BIM proponents claim that in the near future, it will offer a lot of value in terms of (Rahmani Asl et. al, 2013):
- Improving visualization.
- Improving productivity via easy information retrieval.
- Increasing coordination of construction documents.
- Linking of vital information such as vendors for specific materials, location of details and quantities required for tendering.
- Increasing speed of delivery.
- Reducing overall costs.
BIM
Building information modelling and automated quantities technologies can provide the industry with consequential opportunities to raise the quality of the industry to a much higher and sophisticated level. Having the capability to simulate a range of data options with real-time cost advice and carry on throughout the detailed design, construction, and operational stages, BIM will surely place construction practices at a higher value.
منبع : https://www.aproplan.com/blog/quality-management-plan-construction/what-is-bim

زهرا عیسی بیگلو // مهندس معماری // طراح و مدلساز BIM / مدرس رویت مپ Revit MEP